TPACK Model Integration
TPACK model
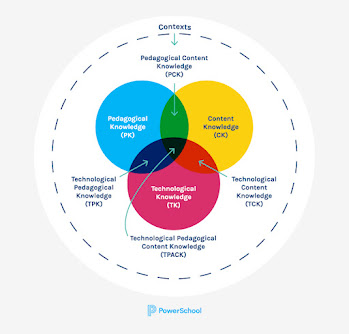
The TPACK model stands for Technological Pedagogical and Content Knowledge. It's a framework for teachers to effectively integrate technology into their classrooms. Here's the breakdown:
- Three Pillars: TPACK combines three types of knowledge that a great teacher needs:
- Technological Knowledge (TK): Understanding the capabilities and limitations of different technologies used for teaching.
- Pedagogical Knowledge (PK): Knowing effective teaching methods and strategies.
- Content Knowledge (CK): Deep understanding of the subject matter being taught.
- The Intersection is Key: The magic happens where these three areas overlap. For example, Technological Pedagogical Knowledge (TPK) refers to the ability to use technology in a way that enhances teaching a specific subject.
- Beyond the Overlaps: TPACK also acknowledges the importance of:
- Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK): Knowing how to teach a specific subject matter in the most effective way.
- Technological Content Knowledge (TCK): Understanding how technology can be used to represent specific content.
By developing all these knowledge areas, teachers can create engaging and effective learning experiences that leverage technology to its full potential.
Understanding TPACK model integration
Lesson Plan (5 steps method)
Name: Dechen Dema Course: B.Ed Primary 1PCB
Class: IV Class Strength: 10 Subject: Mathematics
Period: 1st Period Date: 15/05/2023 Time: 20 minutes
School: Shaba Primary School
Topic: Line of Symmetry
Previous knowledge: Students already some have knowledge on shapes and lines (vertical, horizontal, diagonal)
Teaching Learning Material: Shapes (Rectangle and Parallelogram), 10 A4 size paper, 3 worksheets, 2 shapes for each group (2 x 3= 6 shapes)
Lesson Objectives:
By the end of the lesson, the student will be able to;
i. identify symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes accurately after the activity (cognitive)
ii. draw lines of symmetry for different shapes correctly after the lesson without the help of teacher (psychomotor)
iii. sort the objects in their surrounding into symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes after the teachers explanation (affective)
Anticipatory Set/ Opening
Teacher: “Good morning girls and boys”
Student: “Good morning, madam”
Tr. “How are you all feeling today?”
Std. “Good madam”
Tr. “Any absentees?”
Std. “No, Madam”
Tr. “Good to hear that. Are you all ready for the class?”
Std. “Yes madam”
Tr. “So, you have already learned about lines and 2-D shapes in lower grades, right?”
Std. “Yes, madam”
Tr. “Today our topic is on ‘line of symmetry’. We will see how many line of symmetry does a shape have and shapes which do not have line of symmetry”
Std. “Okay, Madam”
“You will carry out an activity where you have to draw lines of symmetry for the shapes, identify and write which shape is symmetrical and which shape is not symmetrical by folding the shapes.”
Introduction to New Materials
Gaining Attention
After that, the teacher will provide a Content Knowledge (CK) by asking questions like:
Teacher: "What is Symmetry?"
“Symmetry means both sides of the shapes are exactly the same and line of symmetry is basically a line that divides the shapes or objects into two equal halves. For instance, this is a rectangle (shows the shape); I’m dividing this rectangle into two equal parts. The folded line is the dividing line and it is known as the line of symmetry and when I overlap one side of the rectangle to another, it looks exactly the same. Thus rectangle is a symmetrical shape because the halves are exactly the same”
“When I fold this parallelogram, it does not look the same so this shape is not symmetrical and it does not have a line of symmetry. Any object can have the line of symmetry but today we will look into 2-D shapes and find out which shapes have lines of symmetry and which shapes do not.”
Guided Practice (Technology)
Gaining Attention
Providing them the A4 size paper.
Tr. “Let’s take a look at the square shape. First, I want you to draw the square shape in the paper”
“Now cut the square shape with the ruler and see if you can divide this square into two equal parts such that both of the sides looks exactly the same when the shape is folded along a line”
“So this folded line divides the square into two equal parts. When I take one side of the shape to another, the shape overlaps exactly and thus square is a symmetrical shape. A square has more than one line of symmetry, so I want you to find out by folding the square and see how many lines of symmetry a square can have.”
Tr. “Anyone want to share how many lines of symmetry you got for the square?”
After the students share their responses; Tr. “The square have four lines of symmetry because when we fold the square vertically, horizontally or diagonally (left/right) it gives the exact shape as one side of the shape overlap to other side of the shape”
After the teacher’s explanation, Students note down: the square has four lines of symmetry and it is a symmetrical shape.
The teacher will also let the students play quiz on symmetry (Vedantu)
Independent Practice - Collaborated learning (Pedagogical knowledge)
Gaining Attention
Tr. “You will be doing a group activity in which I will be dividing you all into three groups of three member”
Activity Instructions
1. Each group will get two shapes and a worksheet
2. You will have to fold the shape and find out how many line of symmetry the shape have
3. Draw the line of symmetry on the shape provided on the worksheet and write down how many lines of symmetry that shape has
4. You will be given 5 minutes to complete this task
Checking Instruction
One student will repeat the instruction again to the class and if the students are not clear I will repeat the instruction again.
Monitoring
I will go around and see if the students are carrying out the activity or not.
ELA: Students who are done with the earlier activity can come up with their own shapes to see if the shape they had chosen has a line of symmetry or not.
Follow-up Activity
Tr. “From your worksheet, identify which shapes are symmetrical and which shapes are not symmetrical”
The teacher will draw a table on the board.
“Now I want one from each group (Volunteer) to come in front to fill the column in the board. Write the name of the shape which have lines of symmetry under the column symmetrical shape likewise write the non-symmetrical shape”
Tr. “You all have done a wonderful job. Give yourself the Amazing clap”
Lesson Closure
I will call out three students (Volunteer) to draw three symmetrical shapes and their lines of symmetry.
After they are done, I will let the student clap their hands three times, tap their feet three times and say ‘Line of Symmetry’.
Tr. “So today we have learned about shapes which have lines of symmetry and shapes which do not have lines of symmetry. Are you all clear with today’s topic? This is all for today. Thank you class.”
Comments
Post a Comment